Introduction
The world of crypto’s does not spot into the bitcoin world: in the latest years the blockchain technology has developed its use, and a young boy at the age of 19 saw the potential of the instrument and built a strong software capable of using decentralized technology not just for transactions, but useful for every type of work, without the need for passing through intermediates.
What is Ethereum and how does it work?
Ethereum is a decentralized global software platform, invented by Vitalik Buterin, that uses the blockchain technology to create any secured digital technology.
To support the blockchain a token is needed, the Ether (ETH), its cryptocurrency also used as a method of transaction.
Ethereum consists of several key components:
- Smart contracts: they are programmable agreements that run on a blockchain, and allows users to digitilize conditions governing the relationship and interactions between the two parts involved in a transaction. Smart contracts serve as self-regulating protocols that enforce the terms of a contract without the need for intermediaries. These contracts are written in code and stored on the blockchain, ensuring transparency and immutability. Once the conditions within the contract are met, the specified actions take place automatically, eliminating the need for manual intervention or third-party involvement.
- Blockchain: similar to Bitcoin, the Etherum mechanism relies on a blockchain system to store and secure transactions. A blockchain is a chain of blocks that contain the data from transactions, publicly available . In general terms, blockchain allows users to rely on a transparent and reliable system, with censorship resistance and no single point of failure.
- Consensus mechanism: Ethereum and Bitcoin previously shared the same consensus protocol for verifying data and adding it to the blockchain, known as proof-of-work (PoW). This involved mining nodes vying for the chance to append the next block to the blockchain by employing energy-intensive machines. This process occurred approximately every 10 minutes.In 2022, Ethereum underwent a significant transformation known as “The Merge,” transitioning the network to a proof-of-stake (PoS) blockchain. The new PoS system demands users to deposit and lock up 32 ether, the native cryptocurrency of Ethereum, to become network validators. This shift aims to process more transactions per second, consuming 99.95% less energy than PoW version and to reduce barriers for entry people to participate in the network, improving the overall network system.
- Ethereum virtual machine (EVM): it is a machine designed to execute any type of crypto-contract that can be built on the Ethereum blockchain. It operates using a programming language called Solidity, which is written on the EVM for execution. The system’s purpose is to enable the creation of smart contracts and programs that automatically execute their conditions as soon as they are satisfied. In practice, the EVM facilitates the predetermined execution of smart contracts and transactions.
- Ether: ether is the crypto currency used in Ethereum, also called “gas”. Any type of transactions or creation of smart contracts requires ethers to work. The amount of gas to pay is determined by the type of transactions. The more complex the transaction is, the higher the gas fee is.
Like banks, ethereum uses accounts to store the ether:
- EOAs: accounts that normal users use for holding and sending ether
- contract accounts: they hold smart contracts
Users can connect to the network by downloading blockchain software onto their computers. Alternatively, users can generate a private key and create a wallet address to initiate interactions with the blockchain.
Ethereum developments
Vitalik Buterin released his paper about his Ethereum project in 2013. With the release of the crypto, a push was needed to increase the value of the crypto and all the project connected.
The first boom came in 2017, when the ICOa, the initial coin offering, became popular. The pierce of Ethereum spiked around $1,200. Even at that time, many ico’s were discovered as scams, proving the role of Ethereum as an instrument to raise money for startup development: funding projects through direct contributions from individuals, a novel approach to capital formation.
A surge in popularity for Ethereum took place in the summer of 2020, propelled by the advent of decentralized finance (DeFi) applications. These startups emerged as pioneers in offering attractive interest rates on Bitcoin and Ether deposits, enabling collateralized lending, and facilitating cryptocurrency swaps through decentralized exchanges (DEXs). Ethereum’s versatility was once again showcased, extending its reach into traditional finance domains such as lending and collateral management, all without the involvement of banks or brokers.
The most recent and audacious development on Ethereum is non-fungible tokens, or NFTs. Introduced in 2017, NFTs typically represent a digital rendition of an image or artwork, meticulously linked to the Ethereum blockchain to confirm their one-of-a-kind nature. With a single NFT collection fetching a staggering $69.3 million, the NFT market is undeniably experiencing a surge, yet it simultaneously paves the way for a broader spectrum of innovative applications.
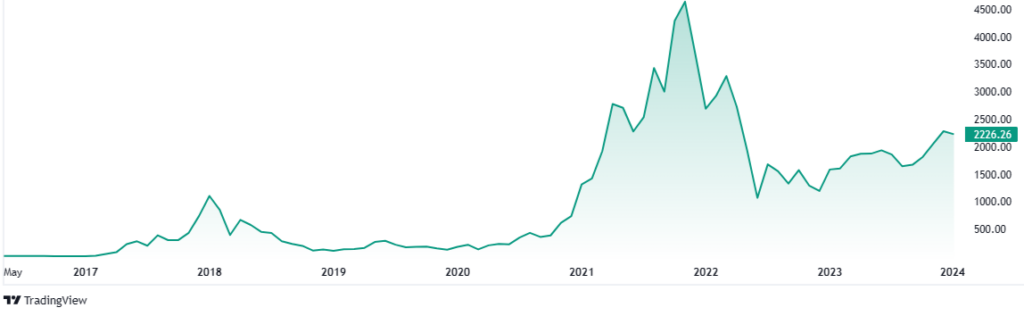
Ethereum today: enthusiasm for a spot ETF?
The recent approval of a spot Bitcoin ETF by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has sent shockwaves through the cryptocurrency market, rekindling hopes for a similar approval for a spot Ether ETF. However, while the SEC’s favorable stance on Bitcoin ETFs has fueled optimism, the regulator has maintained a more cautious approach towards Ethereum ETFs, reportedly adopting a “hard no” stance on these products.
The SEC’s hesitation to approve spot Ethereum ETFs stems from concerns about the potential for market manipulation and fraud. Ethereum is a more complex and volatile asset than Bitcoin, and the SEC is wary of allowing an ETF that could be used to manipulate the market or facilitate illicit activities. Additionally, the SEC is concerned about the lack of transparency in the Ethereum market, which could make it difficult to properly value an ETF based on this asset.
Despite these concerns, some Ethereum ETF issuers remain hopeful that the SEC will eventually change its stance.
Conclusion
Ethereum’s evolution from cryptocurrency to a versatile decentralized platform has been marked by groundbreaking features like smart contracts and the shift to proof-of-stake. Despite regulatory challenges, its role in fostering innovations such as DeFi and NFTs showcases its enduring impact. Ethereum’s ongoing journey signifies resilience and a commitment to pushing the boundaries of decentralized technology, making it a pivotal player in the evolving landscape of cryptocurrencies.
Join ThePlatform to have full access to all analysis and content: https://www.theplatform.finance/registration/
Disclaimer: https://www.theplatform.finance/website-disclaimer/




