Introduction
In recent years, we have witnessed the growth of awareness by both private and institutional subjects of the ongoing climate change and the urgent need to address environmental challenges, such as climate change and energy resource depletion. Dependence on fossil fuels in many countries has led to a vicious cycle of increasing costs, higher energy prices for consumers (as these resources are in short supply) and more pollution that endangered the planet and people’s health.
In response to these concerns, transitioning to renewable energy turned out to be the only way to reduce the impact that human activities have on the environment. These changes have also involved, among others, the financial sector. Nowadays investors are interested more than ever in investing in ESG and climate-aligned strategies and projects that promote environmental protection, renewable energy, and sustainable practices, in order to discourage the use of fossil fuels.
As the demand for renewable energy continues to rise, along with advances in technology and government policies, investments in this sector offer attractive potential returns and long-term growth opportunity.
Investing in the renewable energy market
Renewable energy investments refer to the allocation of financial resources into projects, companies, and technologies that generate power from renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, hydropower, biomass and geothermal energy.
By 2050, about half of global energy production is expected to come from renewable sources, but for this to happen, a huge amount of investment is required in the energy sector.
The sector of renewable energies represents a rapidly expanding sector within alternative investments, playing a crucial role in accelerating the global transition towards clean and sustainable energy sources, diversifying and optimizing the risk-return profiles of institutional investment portfolios within professional investment strategies. What makes them attractive are their potential high returns and a notable independence from financial market fluctuations. For this reason, as the demand for clean energy continues to rise, along with advances in technology and supportive government policies, investors can actively contribute to climate protection and also benefit from the stability of renewable energies.
In the period post Paris Agreement (2015), it has been noted that adding a benchmark index of clean energy and energy-related technologies as a separate asset class to a base portfolio of conventional asset classes improves the performance of the portfolio, by increasing its expected rate of return significantly compared to the increase in risk and demonstrating that investing in this sector is not only a moral choice, but it may also constitute a source of income.
How do the investors play in this sector?
In this context, there are different strategies on which investors can rely on with aim to invest in renewable energy sector. These strategies are differentiated based on their risk-return profile and potential returns, and on investors’ risk tolerance.
Generally, investors invest in the energy sector through equities, mutual funds and also buying energy stocks, which continue to show great prospective returns as oil and gas price continue to rise, but over the years alternative new ways to invest in this field have been put in place.
Other ways used by high-net-worth individuals to invest in this sector are buying and selling energy debt, buying distressed energy assets, and investing in energy hedge funds. This focus is attuned more to high-net-worth individuals who may need both tax deferral benefits and asset diversification into energy stocks, bonds, oil trusts.
Another strategy is to enter into energy options trading, which may provide benefits also in situations of high energy volatility, in which these options could become even more valuable, as they give investors more leverage on higher energy prices.
More speculative investors can invest in all types of energy hedge funds. Nowadays more than a hundred energy hedge funds trades energy commodities, either through exchange-traded futures contracts or over-the-counter price swaps or options, which are more risky.
Several institutional investors are evaluating to invest in this sector through a so-called “fund of funds”, that is less risky and allows to reduce the risks resulting from the volatility.
Advantages and opportunities
Thanks to their macroeconomic importance, renewable energy investments demonstrate a greater resilience to economic downturns and to be less exposed to market fluctuation compared to other asset classes. For this reason, investments in energy sector provide unique advantages compared to those that investors could obtain investing in other sectors. Let’s analyse them more specifically.
- Development of renewable energy: Investing in the green energy sector constitute an incentive to the use of non-fossil energy sources, reducing their costs and increasing their efficiency.
- Diversification of portfolio: Investors can invest in different types of energy-related financial products by balancing traditional energy investments with renewable energy projects, in order to manage the risks that characterised this evolving landscape.
- Long-term perspective: Countries worldwide commit to achieve the energy transition long-term objective, so investments in projects and technologies in line with this goal can yield long-term returns.
- Technological innovation: Progresses in energy infrastructures and technologies create opportunities for investors to support cutting-edge solutions.
- It is an ethical choice, to address environmental concerns.
- Renewable energy could boost the economy by creating jobs.

Risks and challenges
As the energy sector is a constantly evolving sector, it is characterised by continuous changes which can affect the investment value, so it is important that investors carefully assess the main risks associated with energy investment.
- Market volatility: investors may experience sudden and significant changes in the value of their investments, as the energy market is influenced by geopolitical events, changing supply and demand, fluctuations in commodity prices.
- Regulatory Uncertainty : The energy sector is highly regulated, and changes in regulations and tax policies can impact the profitability of energy investments.
- Technological risk: Energy sector includes rapidly changing technologies, that can offer significant returns, but that could also become obsolete rapidly.
- Environmental and Social Risks: Concerns about climate change and sustainability can lead to regulatory changes and can impact investments in this sector, particularly those that involve activities related to fossil fuels.
- Geopolitical tensions and natural disasters: Political instability, wars, sanctions, or tensions in energy-rich regions, but also extreme weather events can affect investment value.
- Financing Challenges: Large-scale energy projects, especially those related to clean energy, often require high upfront spending, making the cost of financing a crucial variable for investors.
- Intermittency of renewable sources: this aspect that characterised renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, poses challenges to stability, so investors need to consider the need for complementary technologies.
- ESG Risks: Investors in the energy sector face increasing scrutiny related to environmental and social standards, that if are not respected can result in reputational and financial risks.
Recent trends and forward perspective
In recent years, we have very often heard about “energy transition”, that is the shift of the global energy sector from fossil-based energy production systems to renewable energy sources. Nowadays, this change is considered more important than ever, as climate changes are worrying individuals as well as institutions, more than ever.
The transition in the energy sector have been and is being supported by technological innovations, which have changed the way to produce and distribute energy in order to reduce the use of fossil fuels, to take full advantage from alternative sources and reduce the impact of human activities on the environment.
In addition, for this change to happen, changes in regulatory landscape are necessary. Over the years, especially last years, governments have encouraged the use of alternative energy sources, through incentives for renewable energy-related activities, feed-in-tariffs, tax credit and subsidies, and fixing carbon price, methods that affect risk-return profile, investment strategies and the energy market.
Analysing the energy market trends in last years, it has been noted that since 2021 annual clean energy investment has risen much faster than investment in fossil fuels. The recovery from the slump caused by the Covid-19 pandemic and the response to the global energy crisis have provided a significant boost to clean energy investment, which have been also boosted by recent periods of strong economic growth and by the increased volatility of fossil fuel prices, especially following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
Valued approximately $7 trillion globally, nowadays energy is the most valuable market segment on earth, responsible for 10% of the world’s annual gross domestic product and it generates more revenue than any other industry.
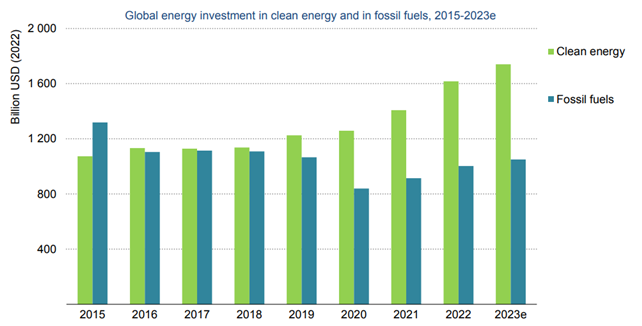
Investment 2023
However, the growth of clean energy investment is not distributed evenly across countries or sectors: more than 90% of these investment since 2021 has come from advanced economies. The macroeconomic environment still presents obstacles, which are holding back investment in many countries, especially developing ones, such as high interest rates, unclear policy frameworks and market designs, financially strained utilities and a high costs of capital. For this reason, international community will have to work hard next years to drive investment in lower-income economies, also because, according to the IEA, global energy demand will grow by more than 30% by 2035 and together with it, also the investment opportunities in this sector.
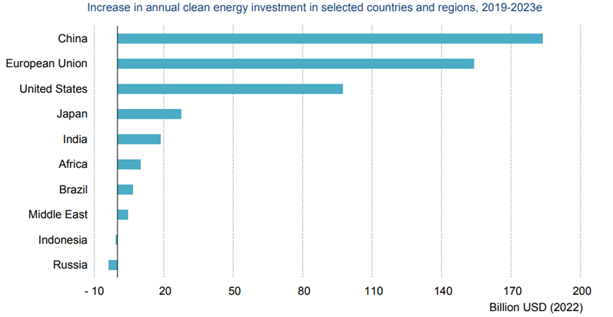
Investment 2023
Despite that, the energy sector will globally grow as well as the investment opportunities, especially because the world needs to spend a total of $8.3 trillion on renewable energy deployment between 2023 and 2030 to align with the Global Net-Zero objective by 2050.
Conclusion
In conclusion, despite the energy market is a complex and volatile ecosystem influenced by different factors, investments in renewable energies prove be an attractive opportunity thanks to their high potential returns and independence from changes in the financial markets. The future of renewable energy investments looks bright. As modern, ecologically developed societies are increasingly demanding sustainable and responsible investment respecting ESG criteria, and are promoting an increasingly massive use of renewable energy, at expense of fossil fuels, investors can actively be part of climate protection and also benefit from the stability of this asset class.
Join ThePlatform to have full access to all analysis and content: https://www.theplatform.finance/registration/
Disclaimer: https://www.theplatform.finance/website-disclaimer/




